Wireless Questions
Question 1
Explanation
Many Cisco access points offer single or double (dual) radio (2.4 and 5.0 GHz).
Note: The wireless controller automates wireless configuration and management functions. It does not connect directly to users.
Question 2
Explanation
Cisco Wireless is designed to provide 802.11 wireless networking solutions for enterprises and service providers. Cisco Wireless simplifies deploying and managing large-scale wireless LANs and enables a unique best-in-class security infrastructure. The operating system manages all data client, communications, and system administration functions, performs radio resource management (RRM) functions, manages system-wide mobility policies using the operating system security solution, and coordinates all security functions using the operating system security framework.
Question 3
Explanation
Star is the most popular topology for Ethernet topology but hub and spoke is the most appropriate WAN topology.
In a Hub-and-spoke network topology, one physical site act as Hub (Example, Main Office or Head Quarter), while other physical sites act as spokes. Spoke sites are connected to each other via Hub site. In Hub-and-spoke topology, the network communication between two spokes always travel through the hub (except when using DMVPN Phase II or Phase III where spokes can communicate with each other directly). The networking device at Hub site is often much more powerful than the ones at spoke sites.
Hub and spoke is an ideal topology when most of the resources lie at the Hub site and the branch sites only need to access to the Hub.
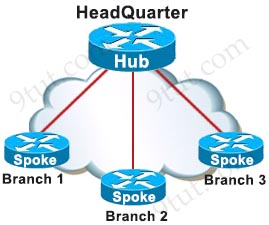 Hub and Spoke topology
Hub and Spoke topology
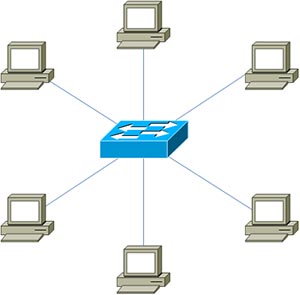 Star topology
Star topology
Note: Although some books may say Hub-and-spoke and Star topologies are the same but in fact they have difference. When talking about Hub-and-spoke we often think about the communication between Hub site and Spoke sites. When talking about Star we think about the communication between end devices.
Question 4
Explanation
WiMAX is short for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. WiMAX is a family of wireless communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards.
Satellite Internet provides Internet access via satellite. It is a form of wireless broadband technology. But it is usually slower than DSL and cable modem.
Municipal wireless network is a city-wide wireless network. This is usually done by providing municipal broadband via Wi-Fi to large parts or all of a municipal area by deploying a wireless mesh network. The typical deployment design uses hundreds of wireless access points deployed outdoors, often on poles.
DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) is a network device, usually at a telephone company central office, that receives signals from multiple customer Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) connections and puts the signals on a high-speed backbone line using multiplexing techniques. It is a cable technology, not a wireless technology.
Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS) is a piece of equipment, typically located in a cable company’s headend or hubsite, which is used to provide high speed data services, such as cable Internet or Voice over Internet Protocol, to cable subscribers. It is a cable technology, not a wireless technology.
Question 5
Explanation
Many rural areas do not have cable Internet access and their only choice to connect to the Internet is via satellite. Satellite internet leverages the hundreds of satellites in orbit around the Earth to send and receive data over the Internet. Of course the speed of this type of connection is much slower than DSL and cable connections. But with new technologies, satellite connections may achieve data speed up to 50 Mbps -> B is correct, D is not correct.
In general, the speeds of popular types of Internet connections are like this: DSL/cable > satellite Internet > dial-up (analog modem).
Satellite Internet uses satellite for Internet connection -> E is not correct
Satellites use radio waves to communicate with the customer’s gateway, also known as a ground station (like a customer’s satellite dish), but not with cellular phone towers -> F is not correct.
For your information, satellite Internet uses high frequency signals, which range from 18.3 gigahertz to 31 gigahertz (Ka band).
Answer A C are two options left and they are acceptable answers. Although in practical they may vary a lot.
Question 6
Explanation
The APIC-EM Path Trace ACL Analysis Tool can display the ACLs that are using (by downloading the configurations after a specific period of time and shows them when we do a path trace). Therefore it helps verify the ACLs more easily.
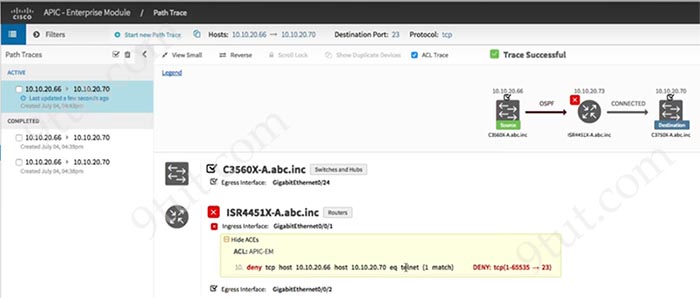
Question 7
Explanation
802.11g is only compatible with 802.11b, not 802.11a so when 802.11a node broadcast, 802.11g access point cannot receive it.
Question 8
Question 9



Q9. Agree with @Daniella
hi all what do you think about the question ;
which two services can be provided by a wireless controller?(choose two)
A. issuing IP addresses to wired devices
B. mitigating threats from the internet
C. providing authentication services to users
D. managing interference in a dense network
E. Layer 3 routing between wired and wireless devices
There are different answers on the different dumbs..
Is the answers correct? In different place I see that most to be DE!!!
After you deploy a new WLAN controller on your network,which two additional tasks should you consider? (Choose two)
A. deploy load balancers
B. configure additional vlans
C. configure multiple VRRP groups
D. deploy POE switches
E. configure additional security policies
Answer: A E