WAN Questions
If you are not sure about WAN, please read our WAN tutorial.
Question 1
Explanation
An example of the output of the “show interface serial …” command is shown below. We can see the line “Encapsulation HDLC”.

Question 2
Explanation
PPP supports both synchronous (like analog phone lines) and asynchronous circuits (such as ISDN or digital links). With synchronous circuits we need to use clock rate.
Note: Serial links can be synchronous or asynchronous. Asynchronous connections used to be only available on low-speed (<2MB) serial interfaces, but now, there are the new HWICs (High-Speed WAN Interface Cards) which also support asynchronous mode. To learn more about them please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/modules/ps5949/ps6182/prod_qas0900aecd80274424.html.
Question 3
Explanation
The advantages of leased lines include:
+ Simplicity: Point-to-point communication links require minimal expertise to install and maintain.
+ Quality: Point-to-point communication links usually offer high service quality, if they have adequate bandwidth. The dedicated capacity removes latency or jitter between the endpoints.
+ Availability: Constant availability is essential for some applications, such as e-commerce. Point-to-point communication links provide permanent, dedicated capacity, which is required for VoIP or Video over IP.
The disadvantages of leased lines include:
+ Cost: Point-to-point links are generally the most expensive type of WAN access. The cost of leased line solutions can become significant when they are used to connect many sites over increasing distances. In addition, each endpoint requires an interface on the router, which increases equipment costs.
+ Limited flexibility: WAN traffic is often variable, and leased lines have a fixed capacity, so that the bandwidth of the line seldom matches the need exactly (therefore answer D is not correct). Any change to the leased line generally requires a site visit by ISP personnel to adjust capacity.
(Reference: Connecting Networks Companion Guide Book published by Cisco Networking Academy – Page 54)
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
The idea behind a WAN is to be able to connect two DTE networks together through a DCE network. The network’s DCE device (includes CSU/DSU) provides clocking to the DTE-connected interface (the router’s serial interface).
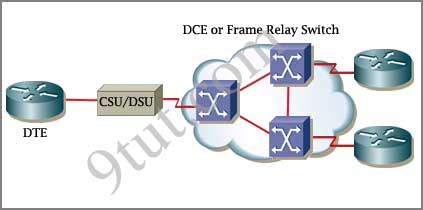
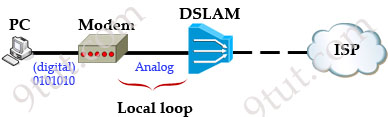
A modem modulates outgoing digital signals from a computer or other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair telephone line and demodulates the incoming analog signal and converts it to a digital signal for the digital device. A CSU/DSU is used between two digital lines -> A & D are correct but B & C are not correct.
For more explanation of answer D, in telephony the local loop (also referred to as a subscriber line) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the carrier or telecommunications service provider’s network. Therefore a modem terminates an analog local loop is correct.
Question 6
Explanation
Below is an example of the output of this command:
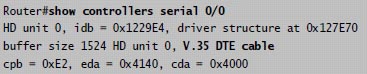
The “show controllers serial …” command tells us about the type of the cable (in the case V.35 DTE cable) and the status of the physical layer of the interface. In above output we learn that there is an cable attached on S0/0 interface. If no cable is found we will see the line “No DTE cable” instead.
Question 7
Explanation
Nowadays all serial links are full-duplex (as serial interfaces have separate Rx & Tx pins) so maybe this question wants to ask about how to check the speed of the serial link. The “show interface” command gives us information about this. An example of this command is shown below:

In this output the speed of S0/0 interface is 1544 Kbits.
Question 8
Explanation
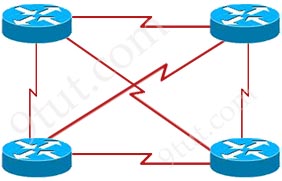
Full-mesh is a network topology in which there is a direct link between all pairs of nodes. Below is an example of full-mesh topology.
Question 9
Question 10
Explanation
A newer fiber-optic media development for long-range communications is called dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM). DWDM multiplies the amount of bandwidth that a single strand of fiber can support.
DWDM circuits are used in all modern submarine communications cable systems and other long-haul circuits.
Specifically, DWDM:
+ Enables bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber -> Answer A is correct
+ Assigns incoming optical signals to specific wavelengths of light (i.e., frequencies)
+ Each channel is capable of carrying a 10-Gbps multiplexed signal -> Answer E is not correct
+ Can multiplex more than 80 different channels of data (i.e., wavelengths) onto a single fiber -> Answer C is not correct
+ Can amplify these wavelengths to boost the signal strength
+ Supports SONET and SDH standards
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2202411&seqNum=6
Question 11
Question 12
Explanation
In a dual-homed setup, the router in a company is still connected to the outside networks via only one ISP, but with two routers or two connections. When one of the dual-homed connection fails, traffic can still flow via other connection so it can tolerate the loss of a network link.
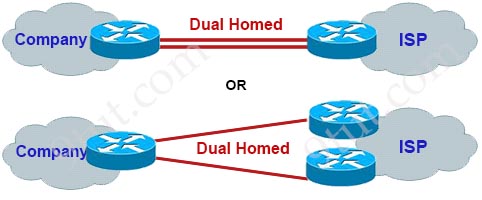
Note: Below is an example of Single Homed setup:




Hi, I am looking for the latest dump for the CCNA 200-125. Can someone please send it to me hghiorsi at aol dot com email.
Thanks in advance.
Hi, I am looking for the latest dump for the CCNA 200-125. Can someone please send it to me kbrar161 dot g mail.
Thanks in advance.