VLAN Questions
Note: If you are not sure about Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN), please read our Virtual Local Area Network VLAN Tutorial.
|
Quick summary about VLAN: Be default all access ports belong to VLAN 1. If we want to assign a new VLAN, we have to use the command “switchport access vlan <vlan-id>” under interface mode. VLAN Benefits: – Logically group devices by department/function, not location so it provides more efficient use of bandwidth The following commands are used to a create a VLAN (for example VLAN 10) and assign it to an interface (for example fa0/1) on a switch: Switch(config)#vlan 10 //Create VLAN 10 first To verify a VLAN or check which ports belong to which VLAN, use the “show vlan” command (or “show vlan id <vlan-id>” for a specific VLAN) |
Question 1
Question 2
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex. Duplex mismatch can easily cause collision domain issue as the device that operates in full duplex mode turns off CSMA/CD. So it is eager to send data immediately without checking if the link is free to use -> A is correct.
An “inband path” is the path which provides path for management traffic (like CDP, VTP, PAgP…) but we are not sure why congestion on the switch inband path can cause collision domain issues. Maybe congestion on inband path prevents the JAM signal (sent when a collision occurs on the link) to be sent correctly on the link.
Question 6
Explanation
If we configure an access port as follows:
| Switch(config)#interface fa0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access |
Then this interface, by default, will belong to VLAN 1. Of course we can assign another VLAN to this port via the “switchport access vlan {vlan-number}” command.
Question 7
Explanation
Traffic on the native VLAN is untagged -> Answer B is not correct.
Control plane traffic (like CDP, VTP, STP…) runs on VLAN 1 by default. They are not blocked on the native VLAN -> Answer C is not correct.
If the answer says “the native VLAN should be set so that no real traffic running on it for security reasons” then it is correct but the native VLAN is not typically disabled -> Answer D is not correct.
CDP runs on VLAN 1 by default and the native VLAN is also VLAN 1 by default so answer A is the best choice here.
Question 8
Explanation
With the configuration above, when we type “do show vlan” we would not see VLAN 10 in the VLAN database because it has not been created yet. VLAN 10 is only created when we exits VLAN configuration mode (with “exit” command).
Question 9
Explanation
IEEE 802.1Q is the networking standard that supports virtual LANs (VLANs) on an Ethernet network. When a frame enters the VLAN-aware portion of the network (a trunk link, for example), a VLAN ID tag is added to represent the VLAN membership of that frame. The picture below shows how VLAN tag is added and removed while going through the network.
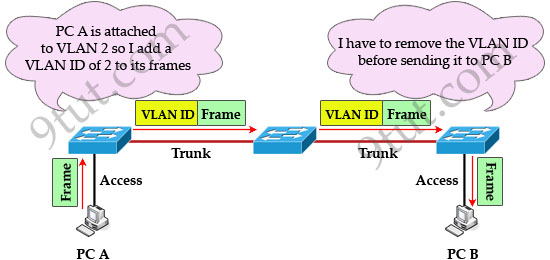
Question 10
Explanation
When using VLAN the number and size of collision domains remain the same -> A is not correct.
VLANs allow to group users by function, not by location or geography -> B is correct.
VLANs help minimize the incorrect configuration of VLANs so it enhances the security of the network -> C is correct.
VLAN increases the size of broadcast domains but does not decrease the number of collision domains -> D is not correct.
VLANs increase the number of broadcast domains while decreasing the size of the broadcast domains which increase the utilization of the links. It is also a big advantage of VLAN -> E is correct.
VLANs are useful but they are more complex and need more administration -> F is not correct.



hi 9tut, about Q5 the right answers should be A and E. any comment !
If problems only occur on that collision domain, and the performance of other collision domains in
the same VLAN is normal, then look at the port counters on the switch to determine what troubles
this segment may be experiencing. Most likely, the cause is simple, such as a duplex mismatch.
Another, less frequent cause is an overloaded or oversubscribed segment.
as Neil reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/virtual-lans-vlan-trunking-protocol-vlans-vtp/23637-slow-int-vlan-connect.html
@9tut, any update on Q5?
@9tut, could you please comment on the question Q5?
I think Q8 is not correct because automatically when you type ‘ vlan 10’ the vlan is added to the vlan database. Try it with PT
I cant see the question text like many others. What is the issue?
Hello,
The questions are there:
https://www.9tut.com/ccna-faqs-a-tips
at point 23.
https://www.9tut.com/ccna-questions-and-answers
how many bits in length is a vlan identifier
Simplest answer for q5
E mentions segment…and this is layer 2 so it should have been frame
correct answer A & C