Topology Architecture Questions
|
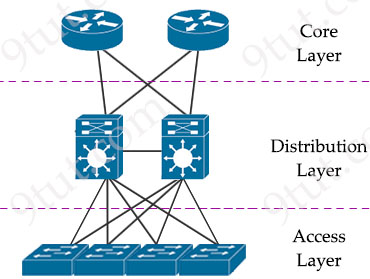
Quick Summary Three tier Architecture The key layers are access, distribution, and core.
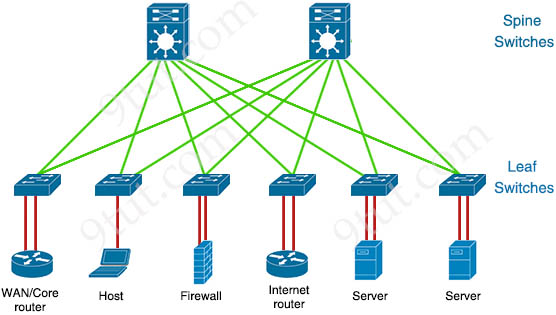
The access layer highlighted grants end devices access to the network. In the WAN environment, it may provide teleworkers or remote sites access to the corporate network across WAN connections. The distribution layer aggregates the data received from the access layer switches before it is transmitted to the core layer for routing to its final destination. The core layer is the network backbone that hierarchically connects several layers of the network design, providing for connectivity between end devices, computing and data storage services located within the data center and other areas, and services within the network. Considerations at the core layer include Spine-leaf Architecture Spine-leaf architecture is typically deployed as two layers: spines (such as an aggregation layer), and leaves (such as an access layer). Spine-leaf topologies provide high-bandwidth, low-latency, nonblocking server-to-server connectivity. With a spine-and-leaf architecture, no matter which leaf switch to which a server is connected, its traffic always has to cross the same number of devices to get to another server (unless the other server is located on the same leaf). This approach keeps latency at a predictable level because a payload only has to hop to a spine switch and another leaf switch to reach its destination. With Leaf-Spine, the network uses Layer 3 routing so STP is no longer required. Spine-leaf architectures rely on protocols such as Equal-Cost Multipath (ECPM) routing to load balance traffic across all available paths while still preventing network loops. This allows all connections to be utilized at the same time while still remaining stable and avoiding loops within the network.
|
Question 1
Explanation
Spine-leaf architecture is typically deployed as two layers: spines (such as an aggregation layer), and leaves (such as an access layer). Spine-leaf topologies provide high-bandwidth, low-latency (-> Answer B is not correct), nonblocking server-to-server connectivity.
With a spine-and-leaf architecture, no matter which leaf switch to which a server is connected, its traffic always has to cross the same number of devices to get to another server (unless the other server is located on the same leaf) (-> Answer A is correct) . This approach keeps latency at a predictable level because a payload only has to hop to a spine switch and another leaf switch to reach its destination.
With Leaf-Spine, the network uses Layer 3 routing so STP is no longer required. (-> Answer C is not correct). Spine-leaf architectures rely on protocols such as Equal-Cost Multipath (ECPM) routing to load balance traffic across all available paths while still preventing network loops. This allows all connections to be utilized at the same time while still remaining stable and avoiding loops within the network.
Question 2
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
The key layers are access, distribution, and core. The core layer is the network backbone that hierarchically connects several layers of the network design, providing for connectivity between end devices, computing and data storage services located within the data center and other areas, and services within the network.
Question 6
Explanation
Ethernet WAN offer the ability of using Ethernet over long-distance links.
Question 7
Explanation
Dual-homed branches (branches connects to two ISPs or one ISP with two connections) increases reliability for the network.
Dynamic routing automatically use backup routes in the case of main routes fail which increases reliability. The configuration is remain unchanged or change a little when we expand the network thus increasing the scalability.
Note: A scalable network can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users
Question 8
Question 9
Explanation
Considerations at the core layer include
+ Providing high-speed switching (i.e., fast transport)
+ Providing reliability and fault tolerance
+ Scaling by using faster, and not more, equipment
+ Avoiding CPU-intensive packet manipulation caused by security, inspection, quality of service (QoS) classification, or other processes
Reference: https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2202410&seqNum=4
Question 10
Explanation
The three-tier hierarchical design maximizes performance, network availability, and the ability to scale the network design.
However, many small enterprise networks do not grow significantly larger over time. Therefore, a two-tier hierarchical design where the core and distribution layers are collapsed into one layer is often more practical. A “collapsed core” is when the distribution layer and core layer functions are implemented by a single device. The primary motivation for the collapsed core design is reducing network cost, while maintaining most of the benefits of the three-tier hierarchical model.
Reference: https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2202410&seqNum=4
A collapsed core network is shown below. The collapsed core network may be deployed with redundant core/distribution router, or consolidated core/distribution router.
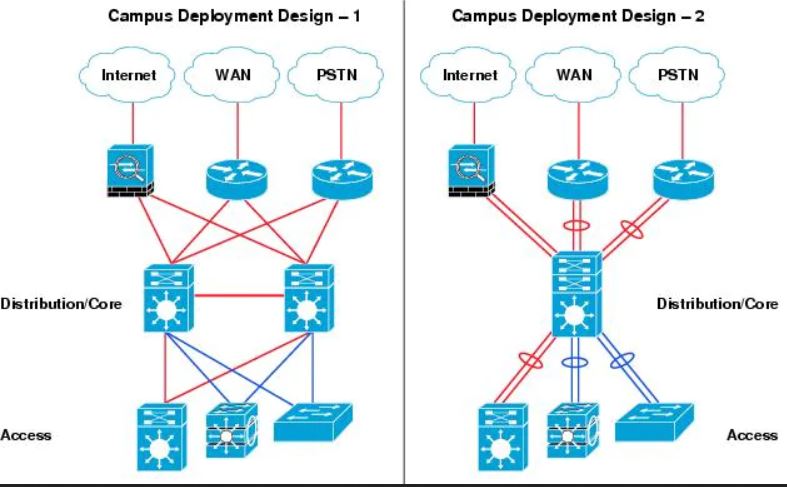
Deploying a collapsed core network results in the distribution layer and core layer functions being implemented in a single device. The collapsed core/distribution device must provide the following:
+ High speed physical and logical paths connecting to the network
+ Layer-2 aggregation and demarcation point
+ Define routing and network access policies -> Answer C is correct
+ Intelligent network services—QoS, Network virtualization, etc.



I love your question
THANK YOU ,I HOPE PASS MY EXAM
Hi Admin,
If i pay the fee did i able to view the all questions.
@NUR: Yes, you can read all the questions with Premium Membership.
how much is membership?
There is an error on the page, I have been trying to access for the last three days but the questions of all of the topics are a blank space
hello
where can i find the question ?
I need a dump for Azur 104
Hope to pass the exam, I’m trying to figure out how to get started and not get overwhelmed.
Thanks 😊 😊
Hi admin
which is the best way to revise
Hi, how can I hide the answers for training purpose?
@Hide the Answers: You can practice with our quizzes. Their links are posted at the top of each page.
Hi All , Im taking the CCNA 200-301 in the next 3 weeks, please anyone with the latest dump can you send them
harley.levi43 at yahoo dot com
Hello, is there any way to get premium membership because I can’t pay with PayPal it doesn’t work in my contry
PLEASE HELP ME 🙏
@A19: Please send an email to support@9tut.com so that we can help you.
cool website, a little 2005 however, maybe an update is needed ;D
@anon: Currently our questions are valid and up to date.
@9tut what changes have occurred or the questions have just been updated ?
there is no questions only explanations
Why is there no test myself link on this topic?
I have found a discrepancy with your answers to question 7 in my VCE player from passleader – I believe the answers are supposed to be Asynchronous Routing & Dual-homed branches. I have a screenshot if you would care to have it.
how to get packet tracer
lovin it.
Hi, there is a way to exercise with this section of ccna 200-301?
Hi, how can i practice with this section of question?
Because here i can’t see the html link page.
@Vincenzo: Please check again, the quiz link is right above “Question 1”.
Hi there 9tut, many of the questions here are not showing. Also, there doesn’t appear to be a quiz link for this section. Please advise.
Thanks.