Switch Questions
|
Quick review of switch function: In brief, the basic switching function at Layer 2 adheres to these rules for determining forwarding responsibility: Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2348264 |
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
The down/down state indicates a Layer 1 problem -> “Protocol mismatch” answer is a Layer 2 problem so it is not correct.
Duplex should be matched on both side but it is not a must -> Therefore “duplex mismatch” is not a correct answer.
The most common Layer 1 problems are faulty or incorrect cabling or hardware failure but none of them is in the answer choices.
If the port is error-disabled, we will see it in down/down state so this answer is correct.
| SW#sh int f1/0/1 FastEthernet1/0/1 is down, line protocol is down (err-disabled) |
There are only two answers left, which are “speed mismatch” and “interface is shut down”. According to the table below (from the old and retired ICND1 100-101 Official Cert Guide), speed mismatch is also a cause of down/down state.
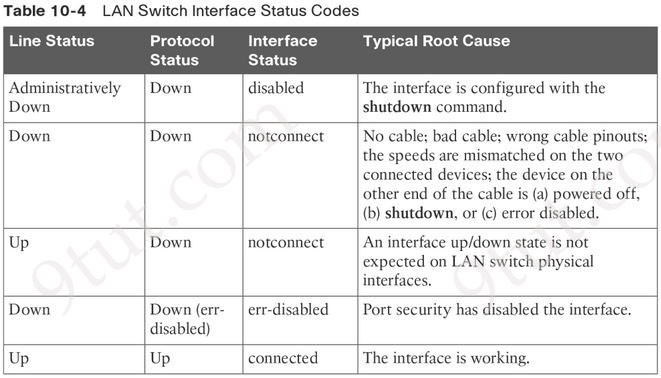
Note:
+ Speed must match between two ends. We tested speed mismatch on real device but we only received “up/down” state.
+ If “interface is shut down” then we will see the “administratively down/down”, not “down/down” state. But the “down/down” state would be seen on the far end interface.
Question 3
Question 4
Explanation
The MAC addresses in the CAM table are the source MAC addresses only. Therefore it only learns MAC address from ingress traffic.



@9tut,
Can you explain answer C (C. moves packets within a VLAN) of Question 3, please?
I thought VLANs are at layer3 and the question is referring at layer 2 switch!! Thanks a lot.
VLANS are on L2 like the Ethernet protocol and these protocols are:
https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/layer-2-protocols.html
anyone who have …….readable book for CCNA 200-301
The SW1 interface g0/1 is in the down/down state. Which two configurations are valid reasons for the interface conditions? (Choose two)
A. There is a duplex mismatch
B. There is a speed mismatch
C. There is a protocol mismatch
D. The interface is shut down
E. The interface is error-disabled
I think about the problem
answer is B and E
Question 2
B and E are the right answers
@HIRO, @Alfie: Yes, thanks for your detection! We reviewed Q2 and corrected them.
Hi, regarding Question 2 :
The SW1 interface g0/1 is in the down/down state. Which two configurations are valid reasons for the interface conditions? (Choose two)
A. There is a duplex mismatch
B. There is a speed mismatch
C. There is a protocol mismatch
D. The interface is shut down
E. The interface is error-disabled
we can understand it better on the CLI :
Router#show ip int br
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 10.2.2.2 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Vlan1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Router#
Thanks,
how to wipe the switch in easy way?
Shah Mohammad Niazy – you do a “write erase” (takes out config file)then make sure your in flash directory and do a “delete vlan.dat” (takes out vlan database/CAM)
I am not able to see the question, I have paid for the premium service, could you please fix this issue as soon as posible
@Anonymous: If your problem still exists, please send an email to support@9tut.com.
Hi guys! Please tell me, If i’m from Russia can I get Cisco certificate?
Hi guys! I’m from somalia how can I learn cisco for my language?
@9tut what does mean by speed mismatch in Question 2?? Does it mean port speed??
@D: Speed means 10Mbps, 100Mbps or 1000Mbps. You can find the speed of the interface with the “show interfaces” (for example: “Full duplex, 100Mb/s”) or “show interface {interface} status”.
Question 3
What are two functions of a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two)
A. makes forwarding decisions based on the MAC address of a packet
B. selects the best route between networks on a WAN
C. moves packets within a VLAN
D. moves packets between different VLANs
E. acts as a central point for association and authentication servers
The problem here is the wording. Switches don’t handle “packets.” They handle frames. Frame would have been the better word choice here.
A & c
I would like to inquire about the reason why option B is considered incorrect in Question 4. My understanding is that switches dynamically learn the MAC addresses of connected devices and store them in the CAM table, which seems consistent with option B. Could you please clarify why this option does not accurately describe the dynamically-learned MAC address feature?
Thank you for your assistance.
@9tut Please explain the above.
@Anonymous, B talks about the connecting CAM table not connected device
how can i register this website is it free or not?
please can someone help me!