STP & VTP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about STP or VTP, please read our Spanning Tree Protocol STP Tutorial, Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP Tutorial, STP Root Port Election Tutorial and VLAN Trunking Protocol VTP Tutorial.
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
The purpose of Port Fast is to minimize the time interfaces must wait for spanning-tree to converge, it is effective only when used on interfaces connected to end stations.
Question 3
Explanation
Enabling the PortFast feature causes a switch or a trunk port to enter the STP forwarding-state immediately or upon a linkup event, thus bypassing the listening and learning states.
Note: To enable portfast on a trunk port you need the trunk keyword “spanning-tree portfast trunk“
Question 4
Explanation
The VTP mode of SW2 is transparent so it only forwards the VTP updates it receives to its trunk links without processing them.
Question 5
Explanation
This bridge is not the root bridge because it does not have the statement “This bridge is the root”. When the local switch is not the root bridge, the port it shows would be the root port to the root bridge. Therefore in this case FastEthernet2/1 is the root port that is connected to the root bridge.
Question 6
Explanation
As this question did not state about bridge priority so we can assume all of them are using the default priority. Therefore the switch with lowest MAC address wins the election.
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
Question 10
Explanation
The keyword here is “always” so we should set the priority to the lowest value which is 0. If we use the “primary root” keyword then our switch is only set to the lower value compared to other switches. And new switch added in the future can be set to lower value than our switch to take over the root role.
Question 11
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit.
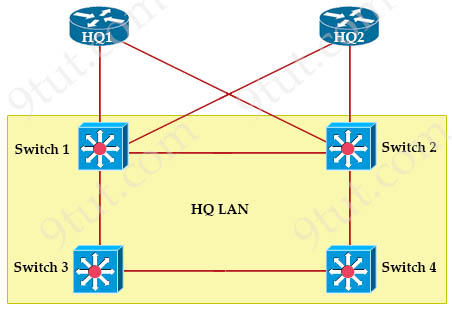
| Switch1: 0C.E0.38.57.24.22 Switch2: 0C.0E.15.22.1A.61 Switch3: 0C.0E.15.1D.3C.9A Switch4: 0C.E0.19.A1.4D.16 |
After the election process what is the root bridge in the HQ LAN?
A. Switch 1
B. Switch 2
C. Switch 3
D. Switch 4
Answer: C
Question 13



I am pretty sure the answer to #2 is B. I have conferred with a few experts and another study guide. You show C here and on the section quizzes.
or maybe not…I am finding information online that also gives the answer you all have. Apparently there is some debate.
I got some explanation on this from an expert. I was told that the “spanning-tree portfast” command does put the port into a an automatic forwarding state BUT it has nothing to do with reloading the switch. Thus, the best answer provided is B (but none of them are really good). Please share if you all have more information.
I also think the correct answer to #2 is B @9Tut
#2 Seems like Answer is C. It immediately puts the port into the forwarding state when the switch is reloaded
Understanding Port Fast
Port Fast immediately brings an interface configured as an access or trunk port to the forwarding state from a blocking state, bypassing the listening and learning states. You can use Port Fast on interfaces connected to a single workstation or server, as shown in Figure 18-1, to allow those devices to immediately connect to the network, rather than waiting for the spanning tree to converge.
Ref:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3560/software/release/12-2_55_se/configuration/guide/3560_scg/swstpopt.html
Regarding #2, B is the correct answer.
When you enable PortFast on a switch or trunk port, the port is immediately transitioned to the spanning tree forwarding state. So C is not correct, because you don’t need to reload the switch to Apply it. Imagine that on production environment, it’s impossible.
Spanning-tree porfast minimizes STP convergence time, because it doesn’t need to recalculate TCN for portfast edge ports.
@Youpi Alex: Thanks for your information, we updated Q.2.
Thanks, i appreciate it!
Hi, I cannot see the questions on this section? Only the explanations?
can some plz explain q#6 and o#12 how they calculate the lowest MAC address plz for RB selection
@haji gul: The explaination for q#6 and #12 are rather strait forward. In both cases you do not have a given bridge-priority, hence we do have to assume, that all switches hold the same priority. This leaves us with the 2nd factor in Bridge-Priority calculation, which is MAC-Address based. Just imagine each MAC-Adress which is only composed of zeros and ones as a binary number. For both questions (q#6&12), the destinguishing factors happen in the 2nd and 4th octett of the MAC-Addresses.
There seems to be an error with q#4 answeres. From the supposed two correct answeres (C&E) only C would be correct (if i am not mistaken). From my expirence a Switch running Rapid PVST+ does state so explicitly in the show spanning-tree output. However, the protocol stated here is RSTP aka. IEEE Rapid Spanning-Tree which does not operate on a per VLAN basis. Hence only one of the provided options answere E would match the given exhibit.
I have to rewoke my last comment. STP Protocol does get promoted as stp or rstp. Per VLAN spanning-tree is just an implementation method used by cisco, but for compatibilty reasons it does only announce itself as rstp.
La pregunta 10 considero que la respuesta es D no A ya que si dos switch tienen la misma prioridad 0 la selección será por la mac, mientras que si se asigna root primary siempre será el root
#5-Answer for Spanning Tree Mode should be Rapid STP (rstp) and not Rapid PVST+ (Rapid PVST+), right?
Question 7 which switch will become the root bridge?
Priority can only be changed by 4096 am I wrong
Can someone help
# show spanning-tree vlan 1
INT Role Status Cost Priority NBR
fa0/2 128.2
What is NBR whats its Role-reason, how do you change config ?
It seems to be just the same as interface this interface
@9tut
It supposed SW2 right that have lowest MAC address? why the answer is SW 3?
Same with the question 6. hurmmm
Switch1: 0C.E0.38.57.24.22
Switch2: 0C.0E.15.22.1A.61
Switch3: 0C.0E.15.1D.3C.9A
Switch4: 0C.E0.19.A1.4D.16
After the election process what is the root bridge in the HQ LAN?
@zack: Switch 3 MAC address is lower than Switch2 MAC because 1 (in 1D.3C.9A) < 2 (22.1A.61).
#2 the correct answer is B. The question says primary effect, even though C is correct but we put the port in that state because we want to reduce the convergence time, so if we read the question properly, the correct answer is B, because it is the primary effect or primary reaction we want when we enable PortFast.
hi where is the exam questions ?
For question 2, the correct answer is B: “to minimize spanning-tree convergence time”. Refer to Cisco website, and to the part headed as “Understanding Port Fast” :https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/metro/me3600x_3800x/trash/swstpopt.html
where it says:
Note Because the purpose of Port Fast is to minimize the time interfaces must wait for spanning tree to converge, it is effective only when used on STP ports connected to end stations. If you enable Port Fast on an interface connecting to another switch, you risk creating a spanning-tree loop.
Where are the questions? Why am i unable to see questions.
I need CCNP question. who can help me? my email is {email not allowed}
my email is: ahmad_mardani2002 at yahoo.com
What is the fee for premium membership?
A really easy way to figure
out the lowest MAC address is to just start reading from the left toward the right until
you find a lesser value…Todd Lammle
please regarding #7 if the Bridge Priority Field can only be set in increments of 4096 how come 30000 is acceptable???the answer should be S1 ????urgent please check
@9tut please regarding #7 if the Bridge Priority Field can only be set in increments of 4096 how come 30000 is acceptable???the answer should be S1 ????urgent please check
@alex: Although Bridge Priority Field can only be set in increments of 4096 but Cisco’s Per-VLAN Spanning-Tree Plus (PVST+) adds the VLAN number (sys-id-ext) to the Bridge Priority so Bridge Priority can be any number. For example, the Bridge Priority of 32770 for VLAN 2 (32768 + 2).