NTP Questions
|
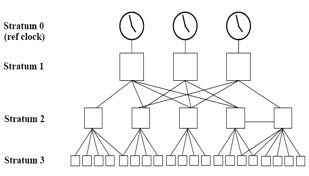
Quick review of NTP NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source, usually a reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum 0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it. Stratum 0 servers cannot be used on the network but they are directly connected to computers which then operate as stratum-1 servers. A stratum 1 time server acts as a primary network time standard.
A stratum 2 server is connected to the stratum 1 server; then a stratum 3 server is connected to the stratum 2 server and so on. A stratum 2 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum 1 server. A stratum 3 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum-2 server… A stratum server may also peer with other stratum servers at the same level to provide more stable and robust time for all devices in the peer group (for example a stratum 2 server can peer with other stratum 2 servers). – NTP is designed to synchronize the time on a network. NTP runs over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), using port 123 as both the source and destination. |
Question 1
Explanation
To configure a Cisco device as an Authoritative NTP Server, use the ntp master [stratum] command.
To configure a Cisco device as a NTP client, use the command ntp server <IP address>. For example: Router(config)#ntp server 192.168.1.1. This command will instruct the router to query 192.168.1.1 for the time.
Question 2
Explanation
Below is the output of the “show ntp status” command. From this output we learn that R1 has a stratum of 10 and it is getting clock from 10.1.2.1.
R1#show ntp status Clock is synchronized, stratum 10, reference is 10.1.2.1 nominal freq is 250.0000 Hz, actual freq is 249.9987 Hz, precision is 2**18 reference time is D5E492E9.98ACB4CF (13:00:25.596 CST Wed Sep 18 2013) clock offset is 15.4356 msec, root delay is 52.17 msec root dispersion is 67.61 msec, peer dispersion is 28.12 msec
Question 3
Explanation
To configure authentication, perform this task in privileged mode:
Step 1: Configure an authentication key pair for NTP and specify whether the key will be trusted or untrusted.
Step 2: Set the IP address of the NTP server and the public key.
Step 3: Enable NTP client mode.
Step 4: Enable NTP authentication.
Step 5: Verify the NTP configuration.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4000/8-2glx/configuration/guide/ntp.html
Note: A trusted NTP server may or may not require a secret key so it is not a “must” in this question.



@9tut
Hey,
Regarding question # 3, A and D That is the answer.
And in other dumps, the answer is D and E.
Is the answer to your questions well-tested?
Bg
@9tut please let us know the right answer of question 3
@dotan, @DAS: We confirm the correct answers of Q.3 are A and D.
@dotan @DAS Q3 option E is wrong because you would use the NTP server’s PUBLIC key not its PRIVATE key.
Only the holder of a private key is supposed to know it…
9tut is a best way to pass CCNA EXAME
somebody can tell…
9tut website it is the best way to pass in CCNA EXAME????
NTP server sims?
Hi guys someone pass the CCNA by using 9tut? is this really a dumps? or some question is not accurate?
Which two pieces of information can you determine from the output of the show ntp status command? (Choose two)
A. whether the NTP peer is statically configured
B. the IP address of the peer to which the clock is synchronized
C. the configured NTP servers
D. whether the clock is synchronized
E. the NTP version number of the peer
Can you point me in the right direction of where this explanation is located? This is all that you mentioned regarding that command…
“– Two most popular commands to display time sources statistics: show ntp status and show ntp associations”
Is the expectation that we use a different resource than this website to answer that question? Just seems strange that you have detailed tutorials about seemingly every topic on here, but very little about NTP. Then of course there is a question about NTP that is not explained.