Miscellaneous Questions
|
Quick Summary Login vs Login Local command We usually see the “login” or “login local” command under line VTY or line console but what are they different? Remember this rule of thumb: With “login” command, we have to configure a password on the local router (with the “password …” command) or we will get the warning: “% Login disbled on line …, until ‘password’ is set”. With “login local” command, we have to configure both username and password with the command “username {username} secret {password}” or the command “username {username} password {password}”. But if we forget to configure username and password, no warning message is shown. |
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
SNMP is an application-layer protocol that provides a message format for communication between SNMP managers and agents. SNMP provides a standardized framework and a common language used for the monitoring and management of devices in a network.
The SNMP framework has three parts:
+ An SNMP manager
+ An SNMP agent
+ A Management Information Base (MIB)
The Management Information Base (MIB) is a virtual information storage area for network management information, which consists of collections of managed objects.
With SNMP, the network administrator can send commands to multiple routers to do the backup.
Question 3
Explanation
Untagged traffic from the device attached to the Cisco IP Phone passes through the phone unchanged, regardless of the trust state of the access port on the phone.
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
The two main elements of an optical fiber are its core and cladding. The “core”, or the axial part of the optical fiber made of silica glass, is the light transmission area of the fiber. It may sometimes be treated with a “doping” element to change its refractive index and therefore the velocity of light down the fiber.
The “cladding” is the layer completely surrounding the core.
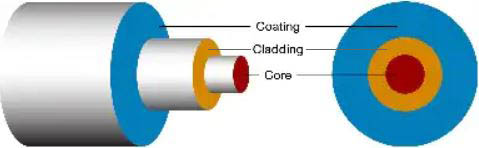
Question 6
Explanation
A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits (or 64th byte) of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are full-duplex/half-duplex mismatch, exceeded Ethernet cable length limits, or defective hardware such as incorrect cabling, non-compliant number of hubs in the network, or a bad NIC.
Late collisions should never occur in a properly designed Ethernet network. They usually occur when Ethernet cables are too long or when there are too many repeaters in the network.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1904.html
Question 7
Explanation
SNMPv3—The most up-to-date protocol focuses on security. SNMPv3 defines a security model, user-based security model (USM), and a view-based access control model (VACM). SNMPv3 USM provides data integrity, data origin authentication, message replay protection, and protection against disclosure of the message payload.
Question 8
Explanation
In this example, the clock time is set to 12:00 am with the clock date of January 1,2020.
R1#clock set 12:00:00 jan 1 2020



Did you study 200-301 only or also 200-125?
@9tut
I would also like an explanation about NetFlow and SNMPv3 question.
Could you please elaborate it?
@9tut
The answer of Q7 is A which is SNMPv3
@9tut, Q7 should be SNMPv3 , without any doubt.
@9tut, Question 7 should be SNMPv3, can you please confirm?
Thanks
who came up with the netflow answer?
@9tut
Please explain why the answer in Q7 is NetFlow
I am agree with SNMPv3.
@all: Thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q7.
Assign an IPv6 GUA using a unique 64-Bit interface identifier” implies what? does this mean use /64 prefix?