Drag Drop Questions
Question 1
Explanation
The focus of Ansible is to be streamlined and fast, and to require no node agent installation. Thus, Ansible performs all functions over SSH. Ansible is built on Python, in contrast to the Ruby foundation of Puppet and Chef.
TCP port 10002 is the command port. It may be configured in the Chef Push Jobs configuration file . This port allows Chef Push Jobs clients to communicate with the Chef Push Jobs server.
Puppet is an open-source configuration management solution, which is built with Ruby and offers custom Domain Specific Language (DSL) and Embedded Ruby (ERB) templates to create custom Puppet language files, offering a declarative-paradigm programming approach.
A Puppet piece of code is called a manifest, and is a file with .pp extension.
Question 2
Question 3
Explanation
The service port can be used management purposes, primarily for out-of-band management. However, AP management traffic is not possible across the service port. In most cases, the service port is used as a “last resort” means of accessing the controller GUI for management purposes. For example, in the case where the system distribution ports on the controller are down or their communication to the wired network is otherwise degraded.
A dynamic interface with the Dynamic AP Management option enabled is used as the tunnel source for packets from the controller to the access point and as the destination for CAPWAP packets from the access point to the controller.
The virtual interface is used to support mobility management, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay, and embedded Layer 3 security such as guest web authentication. It also maintains the DNS gateway host name used by Layer 3 security and mobility managers to verify the source of certificates when Layer 3 web authorization is enabled.
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
SSH uses TCP port 22 while SNMP uses UDP port 161 and 162.
Question 6
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
Explanation
This subnet question requires us to grasp how to subnet very well. To quickly find out the subnet range, we have to find out the increment and the network address of each subnet. Let’s take an example with the subnet 172.28.228.144/18:
From the /18 (= 1100 0000 in the 3rd octet), we find out the increment is 64. Therefore the network address of this subnet must be the greatest multiple of the increment but not greater than the value in the 3rd octet (228). We can find out the 3rd octet of the network address is 192 (because 192 = 64 * 3 and 192 < 228) -> The network address is 172.28.192.0. So the first usable host should be 172.28.192.1 and it matches with the 5th answer on the right. In this case we don’t need to calculate the broadcast address because we found the correct answer.
Let’s take another example with subnet 172.28.228.144/23 -> The increment is 2 (as /23 = 1111 1110 in 3rd octet) -> The 3rd octet of the network address is 228 (because 228 is the multiply of 2 and equal to the 3rd octet) -> The network address is 172.28.228.0 -> The first usable host is 172.28.228.1. It is not necessary but if we want to find out the broadcast address of this subnet, we can find out the next network address, which is 172.28.(228 + the increment number).0 or 172.28.230.0 then reduce 1 bit -> 172.28.229.255 is the broadcast address of our subnet. Therefore the last usable host is 172.28.229.254.
If you are still unclear about how to do subnetting quickly, please read part 3 of our “Subnetting Tutorial – Subnetting Made Easy” at https://www.9tut.com/subnetting-tutorial/3
Question 10
Explanation
Layer 2 Security Mechanism includes WPA+WPA2, 802.1X, Static WEP, CKIP while Layer 3 Security Mechanisms (for WLAN) includes IPSec, VPN Pass-Through, Web Passthrough …
Question 11
Question 12
Explanation
Double-Tagging attack:
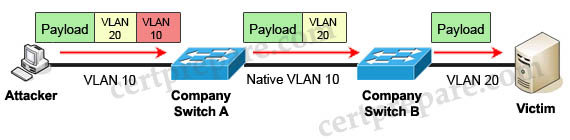
In this attack, the attacking computer generates frames with two 802.1Q tags. The first tag matches the native VLAN of the trunk port (VLAN 10 in this case), and the second matches the VLAN of a host it wants to attack (VLAN 20).
When the packet from the attacker reaches Switch A, Switch A only sees the first VLAN 10 and it matches with its native VLAN 10 so this VLAN tag is removed. Switch A forwards the frame out all links with the same native VLAN 10. Switch B receives the frame with an tag of VLAN 20 so it removes this tag and forwards out to the Victim computer.
Note: This attack only works if the trunk (between two switches) has the same native VLAN as the attacker.
To mitigate this type of attack, you can use VLAN access control lists (VACLs, which applies to all traffic within a VLAN. We can use VACL to drop attacker traffic to specific victims/servers) or implement Private VLANs.
ARP attack (like ARP poisoning/spoofing) is a type of attack in which a malicious actor sends falsified ARP messages over a local area network as ARP allows a gratuitous reply from a host even if an ARP request was not received. This results in the linking of an attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network. This is an attack based on ARP which is at Layer 2. Dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) is a security feature that validates ARP packets in a network which can be used to mitigate this type of attack.
Question 13
Explanation
The “ip route” and “ip addr show eth1” are Linux commands.
+ “ip route”: display the routing table
+ “ip addr show eth1”: get depth information (only on eth1 interface) about your network interfaces like IP Address, MAC Address information
Question 14
Explanation
UDP is a simpler message-based connectionless protocol. In connectionless protocols, there is no effort made to setup a dedicated end-to-end connection.
…
Datagrams – Packets are sent individually and are guaranteed to be whole if they arrive. Packets have definite bounds and no split or merge into data streams may exist.
According to https://community.cisco.com/t5/networking-documents/udp/ta-p/3114870
TCP is connection-oriented and UDP is connectionless. This means that before sending TCP packets, a connection is established between the server and the client. This process of setting up a connection is called TCP handshaking. The stream of packets is then sent over this connection -> TCP transmits packet as stream.
Reference: https://www.vpnmentor.com/blog/tcp-vs-udp/



Can you please update the drag and drops here. I keep running into some on the Comp test and they are not here for me to study them. Thank you!
@9tut PLease update drag and drop here from Composite
@AK: These drag drop questions were included in the Composite Quizzes.
How am I supposed to memorise these answers for the exam, they’re extremely long :(
There are some drag and drop which is in the Composite test not included in this * Drag and drop categories
is it possible to include them here so that we can reference to it
Question 2
Drag and drop the description of file-transfer protocols from the left onto the correct protocols on the right.
I think, TFTP Is used for IOS routers images. Why FTP provides an IOS images?
@9tut: Question 2
Drag and drop the description of file-transfer protocols from the left onto the correct protocols on the right.
I think, TFTP Is used for IOS routers images. Why FTP provides an IOS images?
@Wcfreitas: Both FTP and TFTP can be used to boot IOS image up (https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/cisco-ios-cookbook/0596527225/ch01s08.html). It also provides reliability based on TCP.
Hi I have my CCNA exam on 11th January. When is it good to buy dumps? please reply
would you get partial marks in CCNA exam if you just get a portion of the drag and drop right?
@9tut
@CS: No one knows it. But maybe we will not have partial marks.
@9tut, Q14, TCP breaks the the information into segments and then transmits it, whereas UDP sends the information straightaway in without caring for the sequence. In the answers it is mentioned TCP:Transmits packet as stream and UDP: Transmits packets individually. Kindly check…
@Samby: We have just added additional explanation about stream so please check again.
Hi, I think there is a wrong answer in Question 14. The answer says TCP ‘Transmits packet as stream’ and UDP ‘Transmits packets individually’. In the section TCP and UDP in Question 2 the right answer is ‘TCP provides flow control to avoid overwhelming a receiver by sending too many packets at once, UDP sends packets to the receiver in a continuous stream without checking for sequencing’.
So is the right answer that UDP transmits packets as a stream or TCP?
Please, i don’t understand, where can find the questions please ? here, there is only answers !
Hi, Question 9, line 3, 172.28.228.144 /23. I understand the maths but in a real-world situation can you use a /23 (with an increment of 2) First network address last broadcast address (no usable host)?
Is this just a math question or am I missing something? Or can you use just a network and broadcast address in a particular situation?
Thanks
Patrick
@9tut, In question 13, how to differentiate between the host ip address and the default gateway address ? …
Hi
Can anyone explain to me how this website work ? , cause all I can see is Answers to some questions and labs but never found the questions them selves !!
@9tut
will these drag and drop be exactly how we are doing here in the exam? meaning is it going to have the same (1233) platform or is going to be drag and drop?
@Rick: In the real exam, you can drag and drop the answers to the boxes in any order you like for each group.
@9tut and do they give partial points on drag & drop? Or is it either full or 0 ?
@Alex: We are not sure but maybe you still have partial points for Drag drop.
@9tut i think the correct answer for /25 & /29 is = 172.28.228.114/25 – 172.28.228.1 – 172.28.228.126, 172.28.228.114/29 – 172.28.228.113 – 172.28.228.118
@Homeless Definitely not, 144 = 10010000. For mask /29 (10010|000) (your NET ID is 144) it’ll be still same and first host is 145 until 150, 151 broadcast and 152 is a following NET ID. For mask /25 (1|0000000) you are starting from 129 (your NET ID is 128) last host 254, broadcast 255