DHCP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about DHCP, please read our DHCP tutorial.
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
If we want to get an IP address from the DHCP server on a Cisco device, we can use the command “ip address dhcp”.
Note: The command “ip helper-address” enables a router to become a DHCP Relay Agent.
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
To configure DHCP snooping feature, at least three steps must be done:
| Sequence and Description | Command |
| 1. Configure global DHCP snooping | Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping |
| 2. Configure trusted ports (as least on 1 port). By default, all ports are untrusted |
Switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust |
| 3. Configure DHCP snooping for the selected VLANs | Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan {VLAN-ID | VLAN range} |
Note: To configure DHCP snooping with Dynamic ARP Inspection we need to add the command “ip arp inspection vlan vlan-id” in global configuration mode and “ip arp inspection trust” in interface mode.
In a normal network environment, we should trust interfaces that are connected to routers, not end points.
Question 6
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
Explanation
The following example shows how to configure a DHCP Server on a Cisco router:
| Configuration | Description |
| Router(config)#ip dhcp pool CLIENTS | Create a DHCP Pool named CLIENTS |
| Router(dhcp-config)#network 10.1.1.0 /24 | Specifies the subnet and mask of the DHCP address pool |
| Router(dhcp-config)#default-router 10.1.1.1 | Set the default gateway of the DHCP Clients |
| Router(dhcp-config)#dns-server 10.1.1.1 | Configure a Domain Name Server (DNS) |
| Router(dhcp-config)#domain-name 9tut.com | Configure a domain-name |
| Router(dhcp-config)#lease 0 12 | Duration of the lease (the time during which a client computer can use an assigned IP address). The syntax is “lease {days[hours] [minutes] | infinite}”. In this case the lease is 12 hours. The default is a one-day lease. Before the lease expires, the client typically needs to renew its address lease assignment with the server |
| Router(dhcp-config)#exit | |
| Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.10 | The IP range that a DHCP Server should not assign to DHCP Clients. Notice this command is configured under global configuration mode |
Manual bindings are IP addresses that have been manually mapped to the MAC addresses of hosts that are found in the DHCP database.
All DHCP clients send a client identifier (DHCP option 61) in the DHCP packet. To configure manual bindings, you must enter the client-identifier DHCP pool configuration command with the appropriate hexadecimal values identifying the DHCP client. For example:
| ip dhcp pool SERVER host 172.16.200.100 255.255.255.0 client-identifier 01aa.bbcc.0003.00 default-router 172.16.200.1 ! |
Therefore two requirements for DHCP binding is the IP address and the hardware address (MAC address) of the client. Notice that in the above example “aabb.cc00.0300” is the MAC address of the client while prefix “01” represents the Ethernet media type.
Note: In fact, this question should ask “When implementing a router as a DHCP server, which one of these features must be configured?”. Because we only need to configure either an “address pool” or “manual binding”.
Question 10
Explanation
If the DHCP Server is not on the same subnet with the DHCP Client, we need to configure the router on the DHCP client side to act as a DHCP Relay Agent so that it can forward DHCP messages between the DHCP Client & DHCP Server. To make a router a DHCP Relay Agent, simply put the “ip helper-address <IP-address-of-DHCP-Server>” command under the interface that receives the DHCP messages from the DHCP Client.
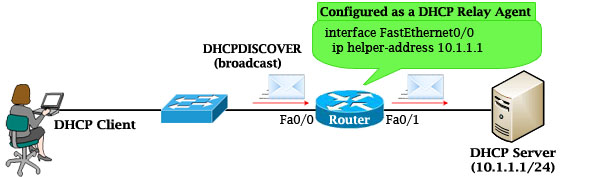
As we know, router does not forward broadcast packets (it drops them instead) so DHCP messages like DHCPDISCOVER message will be dropped. But with the “ip helper-address …” command, the router will accept that broadcast message and cover it into a unicast packet and forward it to the DHCP Server. The destination IP address of the unicast packet is taken from the “ip helper-address …” command.
Question 11



Q4 answers in DHCP section is right BnC where in quiz it comes out wrong? Can someone explain this plz.
@yucare: The commands in Answere B do configure the interface on R2 to forward DHCP requests on the behalf of the actual dhcp Server. Hence working as Man-in-the-Middle for DHCP operation.
The Commands in Answere C do 1st configures R1’s interface faceing towards R2 to make use of DHCP for configuration, aswell as negating the shutdown command applied to all router-ports by default
If you have any questions from Cisco, please leave them to me telegram link Otabek3633
hi, is there same the questions and answer in premium membership?