CCNA – Switch Questions
Here you will find answers about Switch Questions – Part 1
Question 1
Which two commands can be used to verify a trunk link configuration status on a Cisco switch? (choose two)
A. show interfaces trunk
B. show interfaces switchport
C. show ip interface brief
D. show interfaces vlan
Answer: A B
Explanation
The “show interfaces trunk” command and “show interfaces switchport” command can be used to verify the status of an interface (trunking or not). The outputs of these commands are shown below (port Ethernet 1/0 has been configured as trunk):
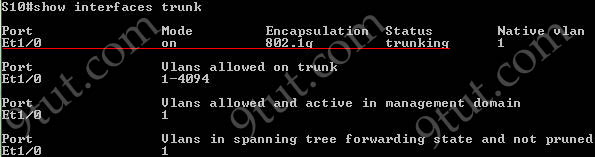
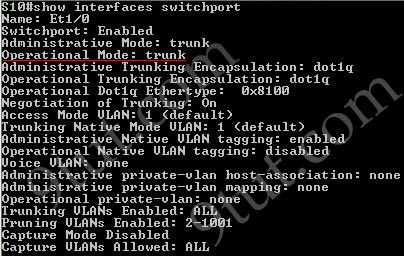
The “show ip interface brief” command only gives us information about the IP address, the status (up/down) of an interface:
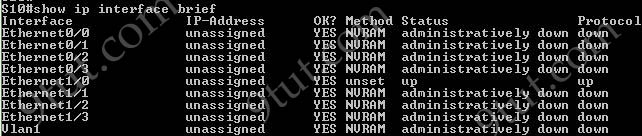
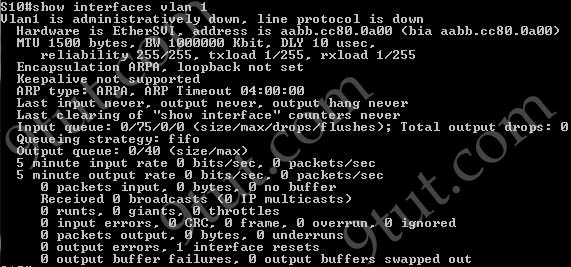
The “show interfaces vlan” command only gives us information about that VLAN, not about which ports are the trunk links:
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. The following commands are executed on interface fa0/1 of 2950Switch.
2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security
2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky
2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1
The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives on interface fa0/1. What two functions will occur when this frame is received by 2950Switch? (Choose two)
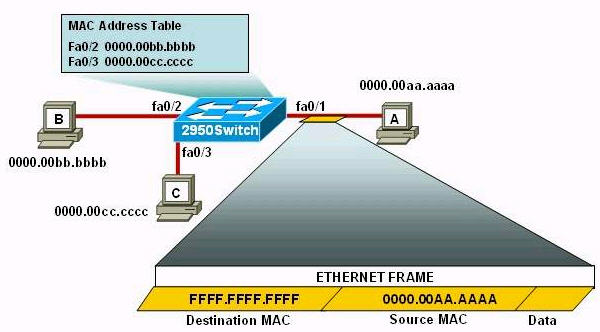
A. The MAC address table will now have an additional entry of fa0/1 FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
B. Only host A will be allowed to transmit frames on fa0/1.
C. This frame will be discarded when it is received by 2950Switch.
D. All frames arriving on 2950Switch with a destination of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be forwarded out fa0/1.
E. Hosts B and C may forward frames out fa0/1 but frames arriving from other switches will not be forwarded out fa0/1.
F. Only frames from source 0000.00bb.bbbb, the first learned MAC address of 2950Switch, will be forwarded out fa0/1.
Answer: B D
Explanation
Please read the explanation at http://www.9tut.net/icnd2/icnd2-operations
Question 3
Which Cisco Catalyst feature automatically disables the port in an operational PortFast upon receipt of a BPDU?
A. BackboneFast
B. UplinkFast
C. Root Guard
D. BPDU Guard
E. BPDU Filter
Answer: D
Explanation
We only enable PortFast feature on access ports (ports connected to end stations). But if someone does not know he can accidentally plug that port to another switch and a loop may occur when BPDUs are being transmitted and received on these ports.
With BPDU Guard, when a PortFast receives a BPDU, it will be shut down to prevent a loop -> D is correct.
Question 4
Why will a switch never learn a broadcast address?
A. Broadcast frames are never sent to switches.
B. Broadcast addresses use an incorrect format for the switching table.
C. A broadcast address will never be the source address of a frame.
D. Broadcasts only use network layer addressing.
E. A broadcast frame is never forwarded by a switch.
Answer: C
Question 5
Which three statements accurately describe layer 2 Ethernet switches? (choose three)
A. Microsegmentation decreases the number of collisions on the network.
B. If a switch receives a frame for an unknown destination, it uses ARP to resolve the address.
C. Spanning Tree Protocol allows switches to automatically share vlan information.
D. In a property functioning network with redundant switched paths, each switched segment will contain one root bridge with all its ports in the forwarding state. All other switches in that broadcast domain will have only one root port.
E. Establishing vlans increases the number of broadcast domains.
F. Switches that are configured with vlans make forwarding decisions based on both layer 2 and layer 3 address information.
Answer: A D E
Explanation
Microsegmentation is a network design (functionality) where each workstation or device on a network gets its own dedicated segment (collision domain) to the switch. Each network device gets the full bandwidth of the segment and does not have to share the segment with other devices. Microsegmentation reduces and can even eliminate collisions because each segment is its own collision domain -> A is correct.
Note: Microsegmentation decreases the number of collisions but it increases the number of collision domains.
D and E are correct based on the theory of STP and VLAN.
Question 6
Switch ports operating in which two roles will forward traffic according to the IEEE 802.1w standard? (Choose two)
A. alternate
B. backup
C. designated
D. disabled
E. root
Answer: C E
Explanation
IEEE 802.1w is the standard of Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). There are 5 port roles in this standard: Root port, Designated port, Alternative port, Backup port and Disabled port. In these 5 port roles, only Root port and Designated port can forward traffic.
Question 7
Select the action that results from executing these commands:
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
A. A dynamically learned MAC address is saved in the startup-configuration file.
B. A dynamically learned MAC address is saved in the running-configuration file.
C. A dynamically learned MAC address is saved in the VLAN database.
D. Statically configured MAC addresses are saved in the startup-configuration file if frames from that address are received.
E. Statically configured MAC addresses are saved in the running-configuration file if frames from that address are received.
Answer: B
Explanation
The full syntax of the second command is:
switchport port-security mac-address sticky [MAC]
If we don’t specify the MAC address (like in this question) then the switch will dynamically learn the attached MAC Address and place it into your running-configuration -> B is correct.
Question 8
What is valid reason for a switch to deny port access to new devices when port security is enabled?
A. The denied MAC addresses have already been learned or configured on another secure interface in the same VLAN.
B. The denied MAC address are statically configured on the port.
C. The minimum MAC threshold has been reached.
D. The absolute aging times for the denied MAC addresses have expired.
Answer: A
Explanation
A security violation occurs in either of these situations:
* When the maximum number of secure MAC addresses is reached on a secure port and the source MAC address of the ingress traffic is different from any of the identified secure MAC addresses, port security applies the configured violation mode.
* If traffic with a secure MAC address that is configured or learned on one secure port attempts to access another secure port in the same VLAN, applies the configured violation mode.
From the second statement we can figure out A is the correct answer. But for your information we will discuss other answers as well.
Answer B is not correct because we can’t configured which MAC address will be denied. We can only configure which MAC is allowed.
We can only configure the maximum MAC threshold, not the minimum threshold -> C is not correct.
The aging times are only configured for allowed MAC addresses, not for denied MAC -> D is correct.
For your information about aging time:
When the aging type is configured with the absolute keyword, all the dynamically learned secure addresses age out when the aging time expires
This is how to configure the secure MAC address aging type on the port:
Router(config-if)# switchport port-security aging type absolute
and configure the aging time (aging time = 120 minutes)
Router(config-if)# switchport port-security aging time 120
When this command is used, all the dynamically learned secure addresses age out when the aging time expires
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SX/configuration/guide/port_sec.html)
Question 9
A network administrator needs to configure port security on a switch. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. The network administrator can apply port security to dynamic access ports
B. The network administrator can configure static secure or sticky secure mac addresses in the voice vlan.
C. The sticky learning feature allows the addition of dynamically learned addresses to the running configuration.
D. The network administrator can apply port security to EtherChannels.
E. When dynamic mac address learning is enabled on an interface, the switch can learn new addresses up to the maximum defined.
Answer: C E
Explanation
Follow these guidelines when configuring port security:
+ Port security can only be configured on static access ports, trunk ports, or 802.1Q tunnel ports.
+ A secure port cannot be a dynamic access port.
+ A secure port cannot be a destination port for Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN).
+ A secure port cannot belong to a Fast EtherChannel or Gigabit EtherChannel port group.
+ You cannot configure static secure or sticky secure MAC addresses on a voice VLAN.
+ When you enable port security on an interface that is also configured with a voice VLAN, you must set the maximum allowed secure addresses on the port to at least two.
+ If any type of port security is enabled on the access VLAN, dynamic port security is automatically enabled on the voice VLAN.
+ When a voice VLAN is configured on a secure port that is also configured as a sticky secure port, all addresses seen on the voice VLAN are learned as dynamic secure addresses, and all addresses seen on the access VLAN (to which the port belongs) are learned as sticky secure addresses.
+ The switch does not support port security aging of sticky secure MAC addresses.
+ The protect and restrict options cannot be simultaneously enabled on an interface.
Note: In fact answer D may be correct but it is unclear according to this link:
“A physical interface with port security enabled can join a Layer 2 EtherChannel only if port security is also enabled on the EtherChannel; otherwise the command is rejected by the CLI.”
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
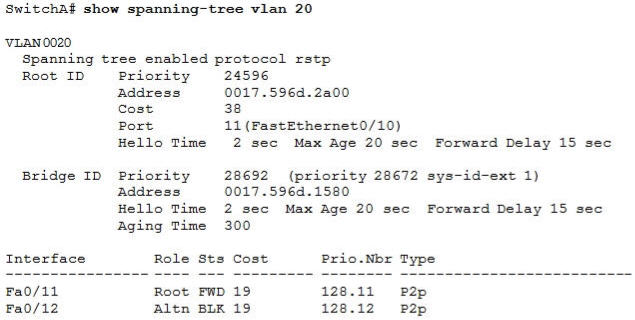
A. The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20.
B. VLAN 20 is running the Per VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol.
C. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.1580.
D. SwitchA is not the root bridge, because not all of the interface roles are designated.
Answer: D
Explanation
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge -> A is not correct.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST -> B is not correct.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00 -> C is not correct.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge -> D is correct.
Question 11
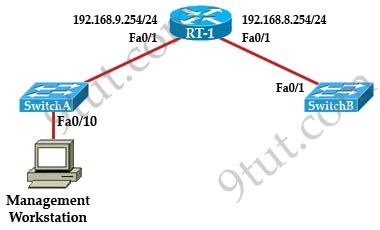
A technician has installed SwithchB and needs to configure it for remote access from the management workstation connected SwitchA. Which set of commands is required to accomplish this task?
A.
SwitchB(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
B.
SwitchB(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
C.
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
D.
SwitchB(config)#ip default-network 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
Answer: B
Explanation
To remote access to SwitchB, it must have a management IP address on a VLAN on that switch. Traditionally, we often use VLAN 1 as the management VLAN (but in fact it is not secure).
In the exhibit, we can recognize that the Management Workstation is in a different subnet from the SwitchB. For intersubnetwork communication to occur, you must configure at least one default gateway. This default gateway is used to forward traffic originating from the switch only, not to forward traffic sent by devices connected to the switch.
Question 12
A network administrator wants to ensure that only the server can connect to port Fa0/1 on a Catalyst switch. The server is plugged into the switch Fa0/1 port and the network administrator is about to bring the server online. What can the administrator do to ensure that only the MAC address of the server is allowed by switch port Fa0/1? (Choose two)
A. Configure port Fa0/1 to accept connections only from the static IP address of the server.
B. Employ a proprietary connector type on Fa0/1 that is incompatible with other host connectors.
C. Configure the MAC address of the server as a static entry associated with port Fa0/1.
D. Bind the IP address of the server to its MAC address on the switch to prevent other hosts from spoofing the server IP address.
E. Configure port security on Fa0/1 to reject traffic with a source MAC address other than that of the server.
F. Configure an access list on the switch to deny server traffic from entering any port other than Fa0/1.
Answer: C E
Explanation
We can”configure the MAC address of the server as a static entry associated with port Fa0/1″ with this command:
Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.00AA.AAAA.AAAA
and “configure port security on Fa0/1 to reject traffic with a source MAC address other than that of the server” with these commands:
Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1 (only allow 1 MAC address and that is the static MAC address)
Also we often define what will the switch do if the security is violated:
Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
Question 13
The network security policy requires that only one host be permitted to attach dynamically to each switch interface. If that policy is violated, the interface should shut down. Which two commands must the network administrator configure on the 2950 Catalyst switch to meet this policy? (Choose two)
A. Switch1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1
B. Switch1(config)#mac-address-table secure
C. Switch1(config)#access-list 10 permit ip host
D. Switch1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
E. Switch1(config-if)#ip access-group 10
Answer: A D


