CCNA – Show Command Questions
Here you will find answers to Basic Command Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined from the output?

A. 192.168.1.2 is local to the router.
B. 192.168.3.1 is local to the router.
C. 192.168.1.2 will age out in less than 1 minute.
D. 192.168.3.1 has aged out and is marked for deletion.
Answer: B
Explanation
The “Age” field in the “show ip arp” command is the age in minutes of the cache entry. A hyphen (-) means the address is local so in this case 192.168.1.1 & 192.168.3.1 are local to this router -> B is correct.
Note: The “Age 0” means that the address was cached less than 1 minute ago.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the “Serial0/0 is down” interface status? (Choose two)

A. A Layer 1 problem exists.
B. The bandwidth is set too low.
C. A protocol mismatch exists.
D. An incorrect cable is being used.
E. There is an incorrect IP address on the Serial 0/0 interface.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The first part of the “Serial0/0 is down, line protocol is down” indicates a layer 1 problem while the second part indicates a layer 2 problem -> A is correct.
Some popular layer 1 problems are listed below:
+ device power off
+ device power unplugged
+ loose network cable connection
+ incorrect cable type
+ faulty network cable
Answer B “The bandwidth is set too low” will not make a layer 1 problem.
Answer C is a layer 2 problem.
Answer E is a layer 3 problem.
Question 3
Which line from the output of the show ip interface command indicates a layer 1 problem?
A. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
B. Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down
C. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up
D. Serial0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Answer: B
Explanation
Same as question 2.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. What is the meaning of the output MTU 1500 bytes?
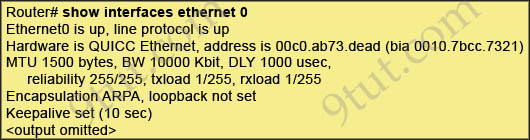
A. The maximum number of bytes that can traverse this interface per second is 1500.
B. The minimum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
C. The maximum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
D. The minimum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
E. The maximum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
F. The maximum frame size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
Answer: E
Explanation
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) defines the maximum Layer 3 packet (in bytes) that the layer can pass onwards.
Question 5
The network administrator normally establishes a Telnet session with the switch from host A. The administrator’s attempt to establish a connect via Telnet to the switch from host B fails, but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful. What is the issue for this problem?
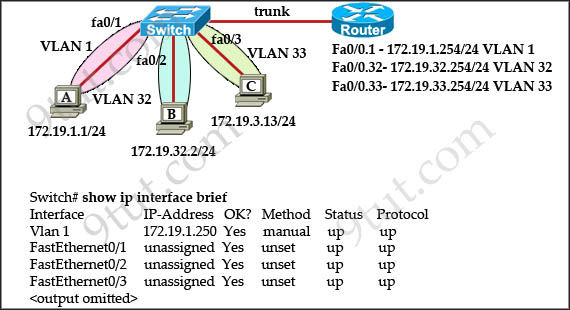
A. Host B and the switch need to be in the same subnet.
B. The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.
C. The switch interface connected to the router is down.
D. Host B need to be assigned an IP address in vlan 1.
Answer: B
Explanation
Updated explanation:
Host A (172.19.1.1) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are in the same subnet so telnet from host A to the switch can be successful even if a default gateway is not set on host A.
But host B (172.19.32.2) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are not in the same subnet. Therefore packets from host B must reach the router Fa0/0.32 interface before forwarding to the switch. But when the switch replies, it does not know how to send packets so an appropriate default gateway must be assigned on the switch (to Fa0/0.32 – 172.19.32.254).
Answer A is not correct because even when host B & the switch are in the same subnet, they cannot communicate because of different VLANs.
Answer C is not correct as host B can ping other two hosts.
Answer D is not correct because host B always belongs to VLAN 32 so assigning an IP address in VLAN 1 does not solve the problem.
Question 6
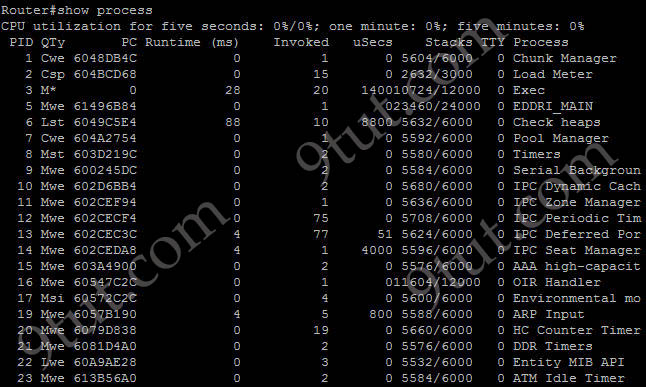
Which command displays CPU utilization?
A. show protocols
B. show process
C. show system
D. show version
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show process” (in fact, the full command is “show processes”) command gives us lots of information about each process but in fact it is not easy to read. Below shows the output of this command (some next pages are omitted)
A more friendly way to check the CPU utilization is the command “show processes cpu history”, in which the total CPU usage on the router over a period of time: one minute, one hour, and 72 hours are clearly shown:
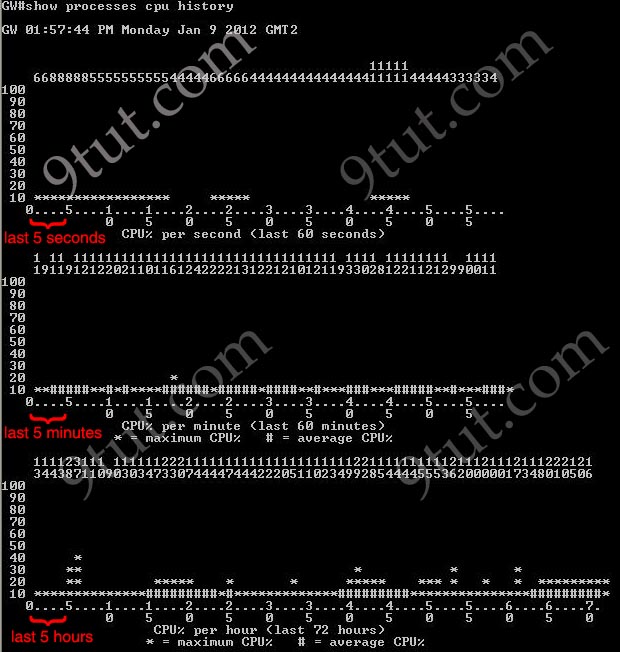
+ The Y-axis of the graph is the CPU utilization.
+ The X-axis of the graph is the increment within the period displayed in the graph
For example, from the last graph (last 72 hours) we learn that the highest CPU utilization within 72 hours is 37% about six hours ago.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. You are connected to the router as user Mike. Which command allows you to see output from the OSPF debug command?

A. terminal monitor
B. show debugging
C. show sessions
D. show ip ospf interface
Answer: A
Explanation
By default, Cisco IOS does not send log messages to a terminal session over IP like Telnet, SSH but console connections do have logging feature enabled by default. To display debug command output and system error messages for Telnet or SSH session, use the “terminal monitor” command in privileged mode.



Домофон=домоффон
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I cling on to listening to the news update lecture about receiving boundless online
grant applications so I have been looking around for the
best site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i get some?