CCNA – Cisco IOS Questions 2
Here you will find answers to Cisco IOS – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about the boot sequence of a router/switch, please read my Cisco Router Boot Sequence Tutorial.
Question 1
When you are logged into a switch, which prompt indicates that you are in privileged mode?
A. %
B. @
C. >
D. $
E. #
Answer: E
Explanation
The “#” (like Switch#) indicates you are in privileged mode while the “>” indicates you are in user mode.
Note: The “#” sign in “Switch(config)#” indicates this is only accessible at privileged EXEC mode. The “(config)#” part indicates we are in configuration mode.
Below lists popular modes in Cisco switch/router:
| Router> | User EXEC mode |
| Router# | Privileged EXEC mode |
| Router(config)# | Configuration mode |
| Router(config-if)# | Interface level (within configuration mode) |
| Router(config-router)# | Routing engine level (within configuration mode) |
| Router(config-line)# | Line level (vty, tty, async) within configuration mode |
Question 2
Which command is used to copy the configuration from RAM into NVRAM?
A. copy running-config startup-config
B. copy startup-config: running-config:
C. copy running config startup config
D. copy startup config running config
E. write terminal
Answer: A
Explanation
The running-config is saved in RAM while the startup-config is saved in NVRAM. So in order to copy the configuration from RAM into NVRAM we use the command “copy running-config startup-config” (syntax: copy).
Question 3
Which command is used to load a configuration from a TFTP server and merge the configuration into RAM?
A. copy running-config: TFTP:
B. copy TFTP: running-config
C. copy TFTP: startup-config
D. copy startup-config: TFTP:
Answer: B
Explanation
The syntax of the copy command is “copy” so to copy a configuration from a TFTP server into RAM we use the command “copy TFTP: running-config”.
Question 4
There are no boot system commands in a router configuration in NVRAM. What is the fallback sequence that router will use to find an IOS during reload?
A. Flash, TFTP server, ROM
B. Flash, NVRAM, ROM
C. ROM, NVRAM, TFTP server
D. NVRAM, TFTP server, ROM
E. TFTP server, Flash, NVRAM
Answer: A
Explanation
When you turn the router on, it runs through the following boot process.
The Power-On Self Test (POST) checks the router’s hardware. When the POST completes successfully, the System OK LED indicator comes on.
The router checks the configuration register to identify where to load the IOS image from. A setting of 0x2102 means that the router will use information in the startup-config file to locate the IOS image. If the startup-config file is missing or does not specify a location, it will check the following locations for the IOS image:
1. Flash (the default location)
2. TFTP server
3. ROM (used if no other source is found)
The router loads the configuration file into RAM (which configures the router). The router can load a configuration file from:
+ NVRAM (startup-configuration file)
+ TFTP server
If a configuration file is not found, the router starts in setup mode.
Question 5
A Cisco router is booting and has just completed the POST process.It is now ready to find and load an IOS image. What function does the router perform next?
A. It checks the configuration register
B. It attempts to boot from a TFTP server
C. It loads the first image file in flash memory
D. It inspects the configuration file in NVRAM for boot instructions
Answer: A
Explanation
Same as Question 4
Question 6
Refer to the partial command output shown. Which two statements are correct regarding the router hardware? (Choose two)
|
system image file is “flash:c2600-do3s-mz.120-5.T1” Cisco 2621 (MPC860) processor (revision 0x600) with 53248K/12288K bytes of memory 32K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory. |
A. Total RAM size is 32 KB
B. Total RAM size is 16384 KB (16 MB)
C. Total RAM size is 65536 KB (64 MB)
D. Flash size is 32 KB
E. Flash size is 16384 KB (16 MB).
F. Flash size is 65536 KB (64 MB)
Answer: C E
Explanation
The line “Cisco 2621 (MPC860) processor (revision 0x600) with 53248K/12288K bytes of memory” tells how much RAM in your router. The first parameter (53248) specifies how much Dynamic RAM (DRAM) in your router while the second parameter (12288K) indicates how much DRAM is being used for Packet memory (used by incoming and outgoing packets) in your router. Therefore you have to add both numbers to find the amount of DRAM available on your router -> C is correct.
Note: Cisco 4000, 4500, 4700, and 7500 routers have separate DRAM and Packet memory, so you only need to look at the first number to find out the DRAM in that router.
The flash size is straightforward from the line “16384K bytes of processor board system flash (Read/Write)” -> E is correct.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1834/products_tech_note09186a00800fb9d9.shtml)
Question 7
Which router IOS commands can be used to troubleshoot LAN connectivity problems? (Choose three)
A. ping
B. tracert
C. ipconfig
D. show ip route
E. winipcfg
F. show interfaces
Answer: A D F
Explanation
The ping command can be used to test if the local device can reach a specific destination -> A is correct.
“tracert” is not a valid command in Cisco IOS commands, the correct command should be “traceroute” -> B is not correct.
The ipconfig command is not a valid command in Cisco IOS too -> C is not correct.
The “show ip route” command can be used to view the routing table of the router. It is a very useful command to find out many connectivity problems (like directly connected networks, learned network via routing protocols…) -> D is correct.
“winipcfg” is an old tool in Windows 95/98 to view IP settings of the installed network interfaces. But it is not a valid command in Cisco IOS commands -> E is not correct.
The “show interfaces” command is used to check all the interfaces on the local device only. It has very limited information to trouble LAN connectivity problem but it is the most reasonable to choose -> F is acceptable.
Question 8
Which two locations can be configured as a source for the IOS image in the boot system command? (Choose two)
A. RAM
B. NVRAM
C. flash memory
D. HTTP server
E. TFTP server
F. Telnet server
Answer: C E
Explanation
The following locations can be configured as a source for the IOS image:
- + Flash (the default location)
- + TFTP server
- + ROM (used if no other source is found)
- (Please read the explanation of Question 4 for more information)
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Why is flash memory erased prior to upgrading the IOS image from the TFTP server?
|
Router# copy tftp flash verifying checksum… OK (0x7BF3) |
A. The router cannot verify that the Cisco IOS image currently in flash is valid
B. Flash memory on Cisco routers can contain only a single IOS image.
C. Erasing current flash content is requested during the copy dialog.
D. In order for the router to use the new image as the default, it must be the only IOS image in flash.
Answer: C
Explanation
During the copy process, the router asked “Erasing flash before copying? [confirm]” and the administrator confirmed (by pressing Enter) so the flash was deleted.
Note: In this case, the flash has enough space to copy a new IOS without deleting the current one. The current IOS is deleted just because the administrator wants to do so. If the flash does not have enough space you will see an error message like this:
| %Error copying tftp://192.168.2.167/ c1600-k8sy-mz.l23-16a.bin (Not enough space on device) |
Question 10
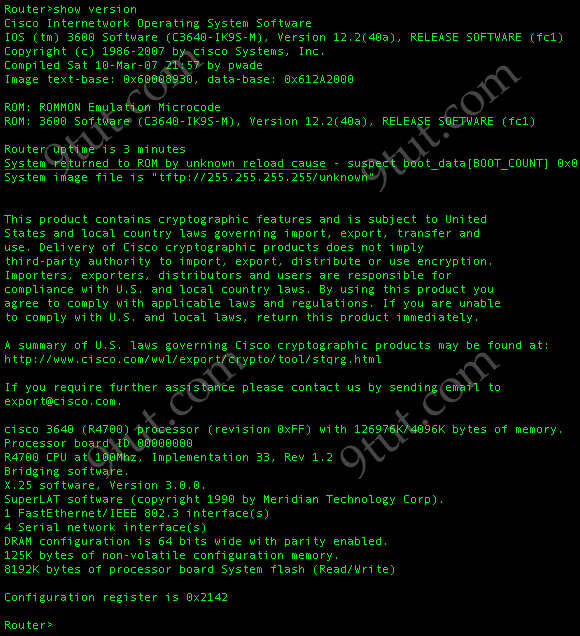
Which command reveals the last method used to powercycle a router?
A. show reload
B. show boot
C. show running-config
D. show version
Answer: D
Explanation
The “show version” command can be used to show the last method to powercycle (reset) a router