CCNA – WAN
Here you will find answers to WAN Questions
If you are not sure about Frame Relay, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
Question 1
The command frame-relay map ip 10.121.16.8 102 broadcast was entered on the router. Which of the following statements is true concerning this command?
A: This command should be executed from the global configuration mode.
B: The IP address 10.121.16.8 is the local router port used to forward data.
C: 102 is the remote DLCI that will receive the information.
D: This command is required for all Frame Relay configurations.
E: The broadcast option allows packets, such as RIP updates, to be forwarded across the PVC.
Correct Answers: E
Explanation:
The command frame-relay map ip 10.121.16.8 102 broadcast means to mapping the distal IP 10.121.16.8 102 to the local DLCI 102. When the “broadcast” keyword is included, it turns Frame Relay network as a broadcast network, which can forward broadcasts
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes DLCI 17?
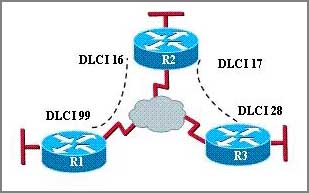
A: DLCI 17 describes the ISDN circuit between R2 and R3.
B: DLCI 17 describes a PVC on R2. It cannot be used on R3 or R1.
C: DLCI 17 is the Layer 2 address used by R2 to describe a PVC to R3.
D: DLCI 17 describes the dial-up circuit from R2 and R3 to the service provider.
Correct Answers: C
Explanation:
DLCI stands for Data Link Connection Identifier. DLCI values are used on Frame Relay interfaces to distinguish between different virtual circuits. DLCIs have local significance because the identifier references the point between the local router and the local Frame Relay switch to which the DLCI is connected.
Question 3
A default Frame Relay WAN is classified as what type of physical network?
A: point-to-point
B: broadcast multi-access
C: nonbroadcast multi-access
D: nonbroadcast multipoint
E: broadcast point-to-multipoint
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) networks are types such as Frame Relay, X.25, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). These networks allow for multi-access, but have no broadcast ability like Ethernet
Question 4
Which of the following are key characteristics of PPP? (Choose three.)
A: can be used over analog circuits
B: maps Layer 2 to Layer 3 address
C: encapsulates several routed protocols
D: supports IP only
E: provides error correction
Correct Answers: A C E
Explanation
Below is some more information about PPP:
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) allows authentication such as Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) and multilink connections (allow several separate physical paths to appear to be one logical path at layer 3) and can be run over asynchronous and synchronous links.
PPP can work with numerous network layer protocols, including Internet Protocol (IP), Novell’s Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), NBF and AppleTalk.
PPP only supports error detection, not error correction so answer E should be understood as “provides error detection”. It is a mistake of this question.
Question 5
Which three Layer 2 encapsulation types would be used on a WAN rather than a LAN? (Choose three)
A: HDLC
B: Ethernet
C: Token Ring
D: PPP
E: FDDI
F: Frame Relay
Correct Answer: A D F
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. What is the meaning of the term dynamic as displayed in the output of the show frame-relay map command shown?

A: The Serial0/0 interface is passing traffic.
B: The DLCI 100 was dynamically allocated by the router
C: The Serial0/0 interface acquired the IP address of 172.16.3.1 from a DHCP server
D: The DLCI 100 will be dynamically changed as required to adapt to changes in the Frame Relay cloud
E: The mapping between DLCI 100 and the end station IP address 172.16.3.1 was learned through Inverse ARP
Correct Answer: E
Explanation
The term dynamic indicates that the DLCI number and the remote router IP address 172.16.3.1 are learned via the Inverse ARP process.
Inverse ARP is a technique by which dynamic mappings are constructed in a network, allowing a device such as a router to locate the logical network address and associate it with a permanent virtual circuit (PVC).
Question 7
Which of the following describes the roles of devices in a WAN? (Choose three.)
A: A CSU/DSU terminates a digital local loop
B: A modem terminates a digital local loop
C: A CSU/DSU terminates an analog local loop
D: A modem terminates an analog local loop
E: A router is commonly considered a DTE device
F: A router is commonly considered a DCE device
Correct Answers: A D E
Explanation
The idea behind a WAN is to be able to connect two DTE networks together through a DCE network. The network’s DCE device (includes CSU/DSU) provides clocking to the DTE-connected interface (the router’s serial interface).
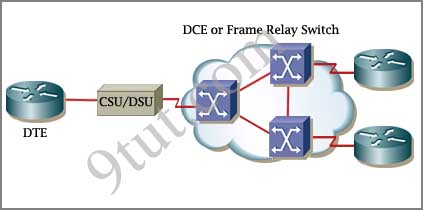
A modem modulates outgoing digital signals from a computer or other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair telephone line and demodulates the incoming analog signal and converts it to a digital signal for the digital device. A CSU/DSU is used between two digital lines -> A & D are correct but B & C are not correct.
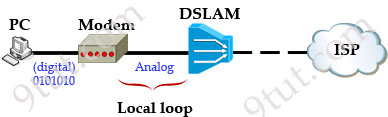
For more explanation of answer D, in telephony the local loop (also referred to as a subscriber line) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the carrier or telecommunications service provider’s network. Therefore a modem terminates an analog local loop is correct.
Question 8
How should a router that is being used in a Frame Relay network be configured to avoid split horizon issues from preventing routing updates?
A: Configure a separate sub-interface for each PVC with a unique DLCI and subnet assigned to the sub-interface
B: Configure each Frame Relay circuit as a point-to-point line to support multicast and broadcast traffic
C: Configure many sub-interfaces on the same subnet
D: Configure a single sub-interface to establish multiple PVC connections to multiple remote router interfaces
Correct Answer: A
Explanation
Look at the figure below:
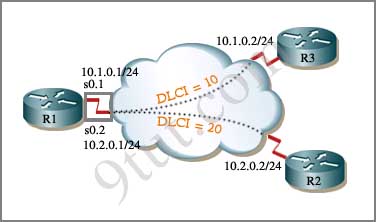
In the figure, router R1 has two point-to-point subinterfaces. The s0.1 subinterface connects to router R3 and the s0.2 subinterface connects to router R2. Each subinterface is on a different subnet.
Question 9
What can a network administrator utilize by using PPP Layer 2 encapsulation? (Choose three.)
A: VLAN support
B: compression
C: authentication
D: sliding windows
E: multilink support
F: quality of service
Correct Answers: B C E
Explanation
Same as question 4
Question 10
The Frame Relay network in the diagram is not functioning properly. What is the cause of the problem?
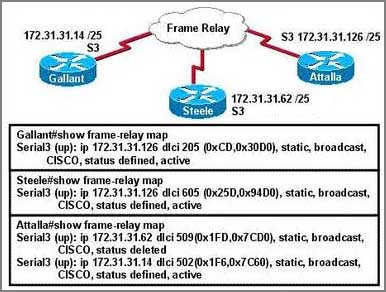
A: The Gallant router has the wrong LMI type configured
B: Inverse ARP is providing the wrong PVC information to the Gallant router
C: The S3 interface of the Steele router has been configured with the frame-relay encapsulation ietf command
D: The frame-relay map statement in the Attalla router for the PVC to Steele is not correct
E: The IP address on the serial interface of the Attalla router is configured incorrectly
Correct Answer: D
Explanation
At Attalla router, we find a deleted status but the next map statement indicates an active status, which if for Gallant. Therefore we can deduce the map statement for the PVC from Attalla to Steele is incorrect. Incorrect DLCI assignments that are configured normally shown up as “deleted” in the frame relay maps.


