CCNA – OSPF Questions 2
Here you will find answers to OSPF Questions – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true about the loopback address that is configured on RouterB? (Choose two)
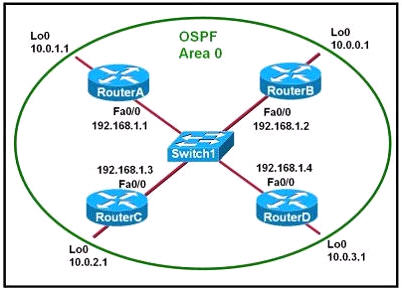
A. It ensures that data will be forwarded by RouterB.
B. It provides stability for the OSPF process on RouterB.
C. It specifies that the router ID for RouterB should be 10.0.0.1.
D. It decreases the metric for routes that are advertised from RouterB.
E. It indicates that RouterB should be elected the DR for the LAN.
Answer: B C
Explanation
A loopback interface never comes down even if the link is broken so it provides stability for the OSPF process (for example we use that loopback interface as the router-id) -> B is correct.
The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
-> The loopback interface will be chosen as the router ID of RouterB -> C is correct.
Question 2
Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A C D
Explanation
Each of routers running link-state routing protocol learns paths to all the destinations in its “area” so we can say A is correct although it is a bit unclear.
Link-state routing protocols generate routing updates only (not the whole routing table) when a change occurs in the network topology so B is not correct.
Link-state routing protocol like OSPF uses Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest path -> C is correct.
Unlike Distance vector routing protocol (which utilizes frequent periodic updates), link-state routing protocol utilizes event-triggered updates (only sends update when a change occurs) -> D is correct but E is not correct.
Question 3
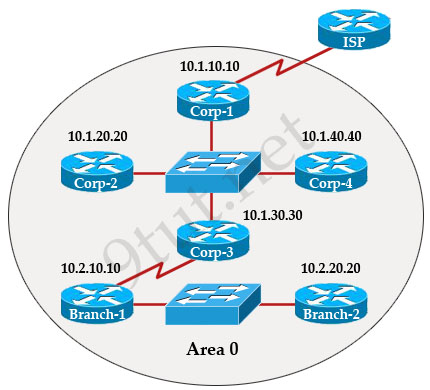
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance.
As part of examining the router resources the OSPF DRs need to be known.
All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router.
Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two)
A. Corp-1
B. Corp-2
C. Corp-3
D. Corp4
E. Branch-1
F. Branch-2
Answer: D F
Explanation
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40) & Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
Question 4
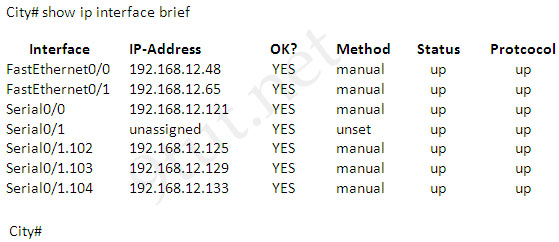
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.
Question 5
When running OSPF, what would cause router A not to form an adjacency with router B?
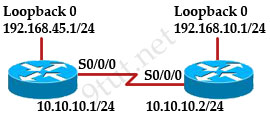
A. The loopback addresses are on different subnets.
B. The values of the dead timers on the routers are different.
C. Route summarization is enabled on both routers.
D. The process identifier on router A is different than the process identifier on router
Answer: B
Explanation
To form an adjacency (become neighbor), router A & B must have the same Hello interval, Dead interval and AREA number.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. The network is converged. After link-state advertisements are received from Router_A, what information will Router_E contain in its routing table for the subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96?
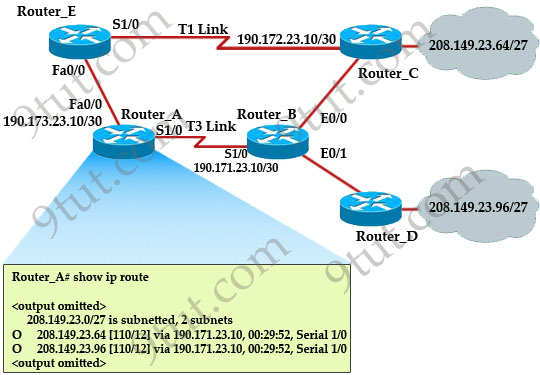
A. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, FastEthernet0/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
B. 208.149.23.64[110/1] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/3] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
C. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
D. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, Serial1/0
Answer: A
Explanation
Router_E learns two subnets subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96 via Router_A through FastEthernet interface. The interface cost is calculated with the formula 108 / Bandwidth. For FastEthernet it is 108 / 100 Mbps = 108 / 100,000,000 = 1. Therefore the cost is 12 (learned from Router_A) + 1 = 13 for both subnets -> B is not correct.
The cost through T1 link is much higher than through T3 link (T1 cost = 108 / 1.544 Mbps = 64; T3 cost = 108 / 45 Mbps = 2) so surely OSPF will choose the path through T3 link -> Router_E will choose the path from Router_A through FastEthernet0/0, not Serial1/0 -> C & D are not correct.
In fact, we can quickly eliminate answers B, C and D because they contain at least one subnet learned from Serial1/0 -> they are surely incorrect.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this RouterD?
RouterD# show ip interface brief

A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.316
Answer: C
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 8
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (choose two)
A. Router(config)#router ospf 1
B. Router(config)#router ospf 0
C. Router(config)#router ospf area 0
D. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
E. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
F. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: A D
Explanation
In the router ospf
command, theranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number -> A is correct but B is not correct.
To configure OSPF, we need a wildcard in the “network” statement, not a subnet mask. We also need to assgin an area to this process -> D is correct.
Question 9
Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
A. Bandwidth, Delay and MTU
B. Bandwidth
C. Bandwidth and MTU
D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay and Load
Answer: B
The well-known formula to calculate OSPF cost is
Cost = 108 / Bandwidth
so B is the correct answer.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. Why are two OSPF designated routers identified on Core-Router?
| Neighbor_ID | Pri | State | Dead Time | Address | Interface |
| 208.149.23.194 | 1 | Full/DR | 00:00:33 | 190.172.32.10 | Ethernet1 |
| 208.149.23.60 | 1 | Full/BDR | 00:00:33 | 190.172.32.10 | Ethernet0 |
| 208.149.23.130 | 1 | Full/DR | 00:00:39 | 190.172.32.10 | Ethernet0 |
A. Core-Router is connected more than one multi-access network
B. The router at 208.149.23.130 is a secondary DR in case the primary fails.
C. Two router IDs have the same OSPF priority and are therefore tied for DR election
D. The DR election is still underway and there are two contenders for the role.
Answer: A
Explanation
OSPF elects one DR per multi-access network. In the exhibit there are two DR so there must have more than one multi-access network.
Question 11
What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 16
B. 2
C. unlimited
D. 4
Answer: D
Explanation
The default number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router is 4. We can change this default value by using “maximum-paths” command:
Router(config-router)#maximum-paths 2
Note: Cisco routers support up to 16 equal-cost paths. In detail, the default number of maximum paths is 32 for Cisco CRS-1 routers and 16 for Cisco XR 12000 Series Routers. The range is from 1 to 32 for Cisco CRS-1 routers and 1 to 16 for Cisco XR 12000 Series Routers.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3.7/routing/configuration/guide/rc37ospf.html)
Question 12
What is the OSPF default frequency, in seconds, at which a Cisco router sends hello packets on a multiaccess network?
A. 10
B. 40
C. 30
D. 20
Answer: A
Explanation
On broadcast multiacess and point-to-point links, the default is 10 seconds. On NBMA, the default is 30 seconds.
Question 13
What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 120
B. 100
C. 90
D. 110
Answer: D
Question 14
What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C


