CCNA EIGRP Lab
Question
Your company has just added R3 router to the existing network. But currently no routing updates are being exchanged between R3 and the network. All other connectivity, including Internet access are working properly.
The task is to identify the fault(s) and correct the router configuration to provide full connectivity between the routers.
All passwords on all routers are set to cisco.
IP addresses are listed in the chart below.
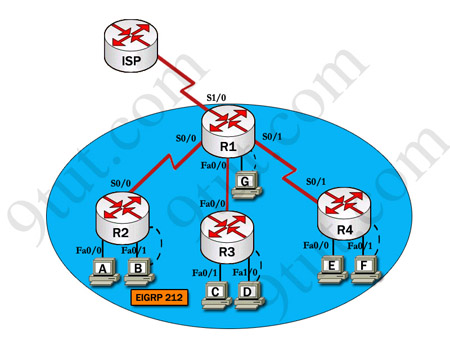
| R1 Fa0/0: 192.168.77.33 S1/0: 198.0.18.6 S0/1: 192.168.60.25 S0/0: 192.168.36.13 |
R2 Fa0/0: 192.168.60.97 Fa0/1: 192.168.60.113 S0/0: 192.168.36.14 |
| R3 Fa0/0: 192.168.77.34 Fa0/1: 192.168.60.65 Fa1/0: 192.168.60.81 |
R4 Fa0/0: 192.168.60.129 Fa0/1: 192.168.60.145 S0/1: 192.168.60.26 |
Answer and explanation
(Note: If you are not sure how EIGRP works, please read my EIGRP tutorial: https://www.9tut.com/eigrp-routing-protocol-tutorial. Note: You can download this sim to practice here: https://www.9tut.com/download/9tut.com_CCNA_EIGRP_sim_question.zip)
We should check the configuration of the new added router first because it does not function properly while others work well. From the command line interface of R3 router, enter the show running-config command
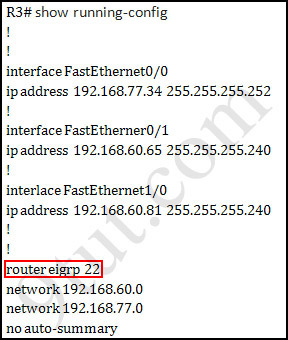
From the output above, we know that this router was wrongly configured with an autonomous number (AS) of 22. When the AS numbers among routers are mismatched, no adjacency is formed.
(You should check the AS numbers on other routers for sure)
To solve this problem, we simply re-configure router R3 with the following commands:
R3>enable (you have to enter Secret@9tut as its password here)
R3#configure terminal
R3(config)#no router eigrp 22
R3(config)#router eigrp 212
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.60.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.77.0
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
R3(config-router)#end
R3#copy running-config startup-config
Check R1 router with the show running-config command:
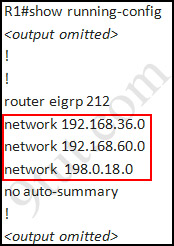
Notice that it is missing a definition to the network R3. Therefore we have to add it so that it can recognize R3 router
R1>enable (you have to enter cisco as its password here)
R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#router eigrp 212
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.77.0
R1(config-router)#end
R1#copy running-config startup-config
Now the whole network will work well. You should check again with ping command from router R3 to other routers!
Modifications:
Maybe in this EIGRP Sim you will see the “passive-interface …” command somewhere in R1 configuration. If the link between R1 to R2; or R1 to R3; or R1 to R4) routers has the “passive interface” then we have to remove it with the “no passive-interface …” command because it prevents EIGRP update from being sent on that interface. But if the “passive interface” is applied to the link between R1 and ISP router like this:
R1:
!
router eigrp 212
passive-interface s1/0
!
then we just leave it. Don’t use the “no passive-interface s1/0” on R1 because the link between R1 & ISP doesn’t need EIGRP to run on it. A static route from R1 to ISP & “ip default-network” command in R1 are correct so that all the routers (R1, R2, R3, R4) can access the Internet.
(Note: The “ip default-network” command in R1 will advertise the static route of R1 (to go to the Internet) to other routers (R2,R3,R4) so that they can access the Internet too). In the exam you will see these lines in R1 configuration:
!
ip default-network 198.0.18.0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 198.0.18.5
!
If you want to learn more about “ip default-network” command please read: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094374.shtml
I read recent comments and realized that you will see the “passive-interface” in the link between R1 & ISP router so just leave it.
Note: Also some readers confuse about if we should use the wildcard masks on the “network” statements under EIGRP process or not. For example should we use:
router eigrp 212
network 192.168.77.0 0.0.0.3
The answer is: we can use wildcard masks or not, it does not matter. Not having a wildcard mask does not make the routes conflicting. The “network …” command in EIGRP (and OSPF, RIP) does not means “advertise this network” but means “If I has interface(s) belongs to this network please turn on EIGRP on that interface. Therefore when you don’t use wildcard mask EIGRP will turn on EIGRP on all interfaces that belongs to the network you specify in the “network …” command.
You should only use wildcard mask on EIGRP if you have 2 or more interfaces that belong to the same major networks but you don’t want to run EIGRP on all of them. For example if your router has 2 interfaces whose IP addresses are 192.168.30.1/28 and 192.168.30.17/28 but you only want to run EIGRP on the first interface, you can type “network 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.15” under EIGRP process.


